How to do Level order traversal in Binary Search Tree
We have see lot of tutorials based on Binary tree and also other traversals like Inorder, Preorder and Postorder etc.,
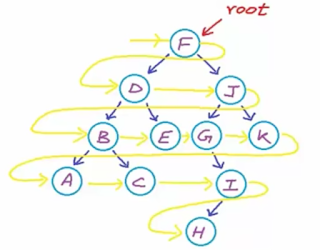
Now in this tutorial lets see how to do Level order traversal of Binary Search Tree using Queue. From the given below tree we need to get output as F, D, J, B, E, G, K, A, C I, H
Solution:
OUTPUT:
Now in this tutorial lets see how to do Level order traversal of Binary Search Tree using Queue. From the given below tree we need to get output as F, D, J, B, E, G, K, A, C I, H
Solution:
- Place the root node in Queue.
- Iterate Queue until queue becomes empty. Dequeue the first node from Queue and print the value of that node.
- Next Enqueue the child nodes left and right nodes inside same queue.
- Repeat the process until each leaf node.
class Node { Node left, right; int data; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } } public class LevelOrderTraversal { public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 11, 6, 19, 4, 8, 5, 43, 49, 10, 31, 17, 5 }; Node root = null; LevelOrderTraversal tree = new LevelOrderTraversal(); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { root = tree.insertNode(root, a[i]); } tree.levelOrderTraversal(root); } public void levelOrderTraversal(Node root) { if (root == null) return; Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.add(root); System.out.println(root.data); while (queue.size() > 0) { Node current = queue.poll(); if (current.left != null) { System.out.println(current.left.data); queue.add(current.left); } if (current.right != null) { System.out.println(current.right.data); queue.add(current.right); } } } public Node insertNode(Node root, int data) { Node currentNode = new Node(data); if (root == null) { root = currentNode; } else { insertData(currentNode, root); } return root; } public Node insertData(Node newNode, Node root) { if (root.data < newNode.data) { if (root.right == null) { root.right = newNode; } else { return insertData(newNode, root.right); } } else if (root.data > newNode.data) { if (root.left == null) { root.left = newNode; } else { return insertData(newNode, root.left); } } return root; } }
OUTPUT:
11 6 19 4 8 17 43 5 10 31 49