Cool !!! How to find the diameter of a binary tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root. The length of path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
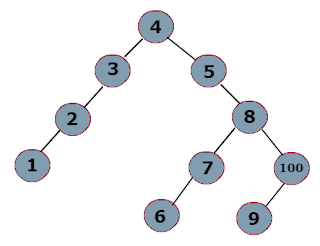
From the given below Binary tree diameter for both will be 9.
Lets see simple java code to create binary tree with the given array of integers and need to find the diameter of that.
OUTPUT:
From the given below Binary tree diameter for both will be 9.
Lets see simple java code to create binary tree with the given array of integers and need to find the diameter of that.
class BST {
BST left, right;
int data;
public BST(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTreeDiameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int val[] = new int[] { 18,10,20,22,4,13,3,12,14,2,1,11,15,16,17 };
BinaryTreeDiameter obj = new BinaryTreeDiameter();
BST root = obj.createBinaryTree(val);
System.out.println("Diameter : "+obj.findDiameter(root));
}
public int findDiameter(BST root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int h1 = getHeight(root.left) + getHeight(root.right);
int lh = findDiameter(root.left);
int rh = findDiameter(root.right);
return Math.max(h1, Math.max(lh, rh));
}
public int getHeight(BST root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int lh = getHeight(root.left);
int rh = getHeight(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(lh, rh);
}
public BST createBinaryTree(int[] val) {
BST root = new BST(val[0]); // Initialize root with 1ft element
BST tmpRoot = root; // Temporary root node
for (int i = 1; i < val.length; i++) {
BST lastNode = getLastNode(tmpRoot, val[i]);
if (val[i] > lastNode.data) {
BST tmp = new BST(val[i]);
lastNode.right = tmp;
} else {
BST tmp = new BST(val[i]);
lastNode.left = tmp;
}
}
return root;
}
public BST getLastNode(BST root, int val) {
if (val > root.data) {
if (root.right == null) {
return root;
} else
return getLastNode(root.right, val);
} else {
if (root.left == null) {
return root;
} else
return getLastNode(root.left, val);
}
}
}
OUTPUT:
Diameter : 9