In our earlier tutorial we have seen about Spring + Hibernate with simple example. Now lets see sample example with Spring JDBC by using DataSource. For more notes on Spring JDBC you can refer to spring doc link.
Here we used MySql database to demonstrate this example.
pom.xml
Employee.java
EmpDao.java
EmpDaoImpl.java
spring-jdbc.xml
MyTestClass.java
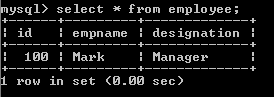
OUTPUT:
Here we used MySql database to demonstrate this example.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.app.spring.datasource</groupId> <artifactId>springdatasource</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>4.1.6.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.35</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>4.1.6.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
Employee.java
package com.app.model; public class Employee { private int id; private String empName; private String designation; public Employee(int id, String empName, String designation){ this.id = id; this.empName = empName; this.designation = designation; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getEmpName() { return empName; } public void setEmpName(String empName) { this.empName = empName; } public String getDesignation() { return designation; } public void setDesignation(String designation) { this.designation = designation; } }
EmpDao.java
package com.app.dao; import com.app.model.Employee; public interface EmpDao { public void insert(Employee emp); }
EmpDaoImpl.java
package com.app.dao; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import com.app.model.Employee; public class EmpDaoImpl implements EmpDao { private DataSource dataSource; public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } public void insert(Employee emp) { String query = "INSERT INTO employee (id, empname, designation) VALUES (?, ?, ?)"; Connection con = null; try { con = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement(query); ps.setInt(1, emp.getId()); ps.setString(2, emp.getEmpName()); ps.setString(3, emp.getDesignation()); ps.executeUpdate(); ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { if (con != null) { try { con.close(); } catch (SQLException e) {} } } } }
spring-jdbc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/roboticapp" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> </bean> <bean id="empDS" class="com.app.dao.EmpDaoImpl"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> </beans>
MyTestClass.java
package com.app; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.app.dao.EmpDao; import com.app.model.Employee; public class MyTestClass { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-jdbc.xml"); EmpDao object = appContext.getBean(EmpDao.class); Employee emp = new Employee(100, "Mark", "Manager"); object.insert(emp); appContext.close(); } }
OUTPUT: